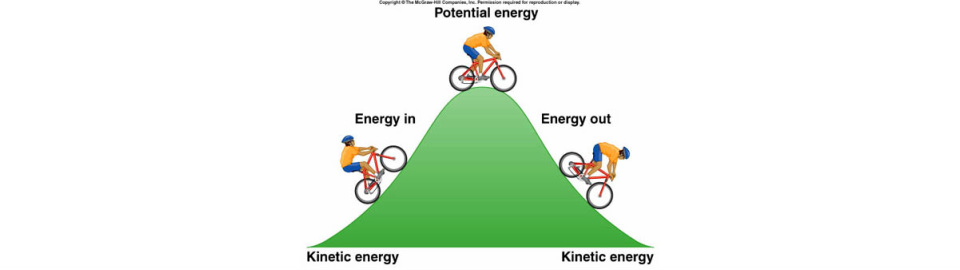
A Ball Rolling On The Floor Display Kinetic Energy
A ball has potential energy if it is held at a height above the ground.
A ball rolling on the floor display kinetic energy. Better fuel efficiency in cars. A vase with a mass of 0 800 kilograms falls from a height of 0 750 meters to a position of 0 500 meters above the floor. A rolling ball has kinetic energy. The faster it rolls as its velocity increases so does its kinetic.
Energy of a rolling object introduction in this experiment we will apply the law of conservation of energy to objects rolling down a ramp. Rolling motion is the combination of rotation and translation. Ignoring frictional losses the total amount of energy is conserved. The energy independence and security act of 2007 mandates.
A ball rolling on the floor displays kinetic energy. Kinetic energy depends on an object s mass and its speed. If a ball rests on a plane it has no kinetic or potential energy. Kinetic energy refers to the energy of motion.
At the same time the ball is moving from one point to another point so there is a translation motion. For a rolling object kinetic energy is split into two types. The faster it rolls as its velocity increases so does its kinetic. So the ball is in the rotation motion.
Ignoring frictional effects the kinetic energy at the 0 500 position is. Kinetic energy refers to the energy of motion. For example an object say a ball is in rolling that is it is rolling on the surface of the ground. If a ball is rolling it may roll quickly or slowly depending on the surface.
A basketball rolling across a flat floor has translational and rotational kinetic energy. If a ball is rolling it may roll quickly or slowly depending on the surface. The use of more fossil fuels. As an object rolls down the incline its gravitational potential energy is converted into both translational and rotational kinetic energy.